Dc charging is gaining popularity as electric vehicles (EVs) move toward an era of fast charging. The reason: Dc fast chargers help EV batteries charge faster. However, dc charging comes with challenges. This article will review four complications that dc charging faces.
Figure 1 shows an insight into the ac and dc charging of an EV. An ac charger has different connectors and power levels than a dc charger. A dc charger bypasses an additional onboard charger placed inside the EV. The onboard charger is meant for converting ac to dc and is typically meant for ac charging.
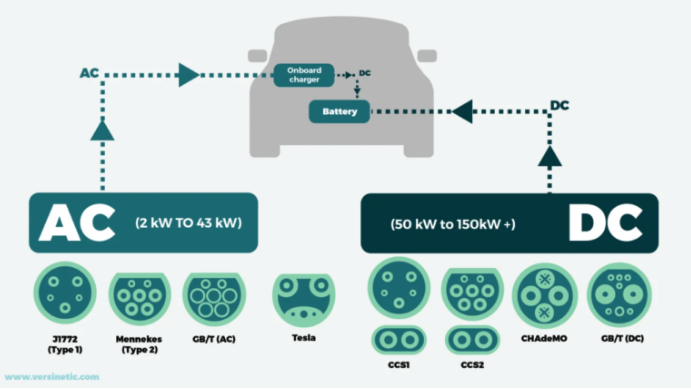
Figure 1. An illustration of ac versus dc charging of an electric vehicle. (Image: Versinetic)
Higher Power Level
The fundamental difference between dc and ac charging is the power levels. Ac charging is widespread in most EV charging cases, especially for two-wheelers. However, with range anxiety among EV users, the need for high-capacity batteries has necessitated high-power charging.
In one of our previous FAQs, we discussed the different power levels for different types of charging. For higher power levels, particularly Level 3, dc charging is the preferred method of EV charging.
However, high power levels come with associated challenges. One such challenge is the safety of the entire charging system. Any unforeseen situation can quickly escalate into a fire accident, so it’s necessary to place more emphasis on safety protocols.
Converter and Inverter Requirement
A dc charging system requires at least one power electronics converter to change the incoming ac supply from the power grid into a dc supply. These converters are rated for heavy power ratings because of the higher EV battery power rating. It leads to a bulkier charging system. Additionally, the cost of the charging infrastructure also increases.
Dc power can also be converted to ac power for motoring, meaning multiple ac-to-dc conversions and back to ac increase the converter count. Such a converter count increase leads to efficiency losses and adds to the financial burden.
Communication Protocols
Communication protocols also make dc more complicated than ac charging. For example, a low-level communication protocol helps indicate the battery’s charging state. For this purpose, a suitable PWM controller is used, where different voltage levels denote the state of the EV.
On the other side, high-level communication — such as PLC and CAN — helps manage charging sequences, assess compatibility issues, and manage payments. Ac charging does not have such a multi-level communication protocol, which makes dc charging more complex.
Standards
Various standards govern the dc charging of EVs. Those include the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC). There are many other standards, but the ISO and the IEC are the primary ones.
Figure 2 shows the different standards applicable to the dc EV charging station and the battery management system. These standards set the various guidelines, operating conditions, and other necessary specifications for proper dc charging. Ac charging, on the other hand, has only a few basic standards.
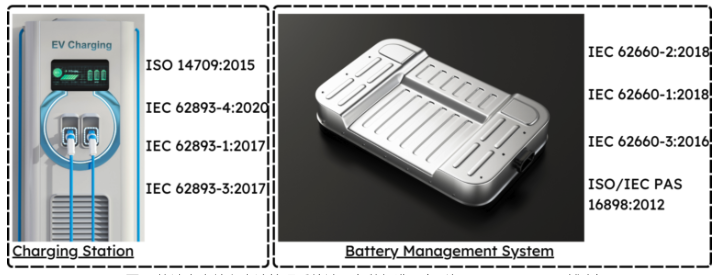
Figure 2. There are various standards involved in a fast-charging station and a bat
Reposted from the WeChat official account:qicheyanjiuyuanauto
