Before the pandemic impacted all our lives, the significant advantages of Industry 4.0 and its added value in achieving operational excellence had already been realized. As digital disruption and technological changes affect the entire ecosystem, recent evidence shows that about 94% of organizations believe that Industry 4.0 helps facilitate smooth operations.
Key Market Trends
The Industry 4.0 market is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 20.6% between 2021 and 2026. The rapid adoption of artificial intelligence (AI) and the Internet of Things (IoT), the increasing demand for robots across various industries, increased government investments in technological advancements, emerging trends, and the use of blockchain and digital currencies are some of the main factors driving the growth and adoption of Industry 4.0 technologies across industries.
Let's go
Applications of Industry 4.0 in the Automotive Sector
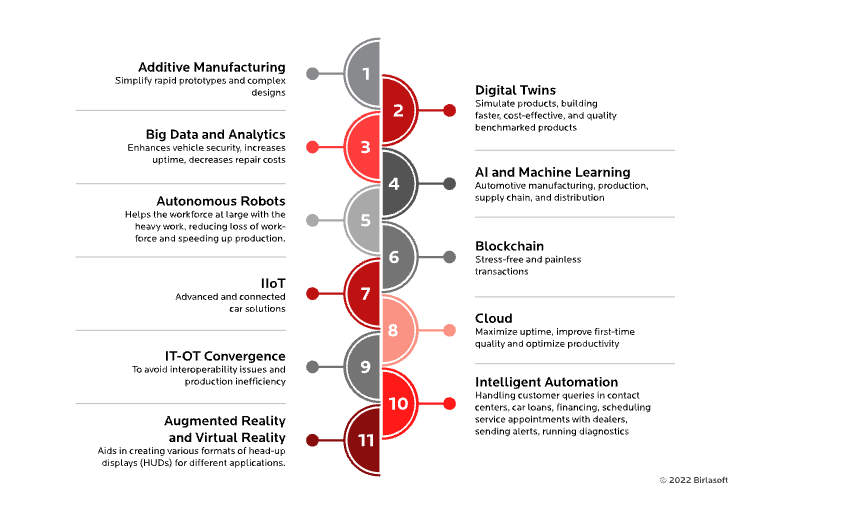
Image sourced from the internet
Additive Manufacturing
From fuel-efficient, powerful cars to the emergence of electric vehicles, the automotive industry is undergoing breakthrough changes with the arrival of Industry 4.0. One of the significant developments is the rise of additive manufacturing or 3D printing.
This cutting-edge and rapidly evolving technology enables designers to create prototypes quickly and simplify complex designs that are difficult to achieve through traditional subtractive manufacturing processes. This new technology offers the automotive industry design and innovation freedom, making the supply chain more efficient. Additionally, it provides an optimized, cost-effective method to test, manufacture, manage, and assemble vehicle parts.
Digital Twins
"Digital twins" are a data-driven manufacturing concept that allows manufacturers and enterprises to simulate products and build faster, more cost-effective, and quality-driven products.
In the automotive sector, a digital twin is a virtual replica of an entire vehicle, mirroring its software, mechanical, electrical, and physical characteristics. It includes real-time sensors, performance metrics, inspection data, service history, configuration changes, warranty, and replacement data.
Big Data and Analytics
Cost pressures, intense competition, market fluctuations, and sudden disruptions have always been challenges for the automotive industry. Big data and analytics serve as powerful tools to uncover incredible opportunities. When used correctly, analytics can significantly aid the automotive sector in various aspects, such as enhancing vehicle safety, increasing uptime, reducing maintenance costs, and more.
Artificial Intelligence in the Automotive Sector
Artificial Intelligence (AI) utilizes data and algorithms to replicate human intelligence and problem-solving abilities. It aids various sectors in solving problems independently. AI is widely applied in automotive assembly and across the value chain.
Currently, AI is being used in design thinking, vehicle manufacturing, production, supply chain, and distribution. It is also employed in developing "driver assistance" and "driver risk assessment" systems, which are transforming and enhancing road safety. AI also plays a role in predictive maintenance and aftermarket services like insurance.
Autonomous Robots
For decades, the automotive industry has utilized robots on its production and assembly lines. This technology has enabled the sector to become more efficient, precise, and agile in its processes. Furthermore, the use of robots in tasks such as vision, spot and arc welding, painting, sealing and coating, internal logistics, and material repair and removal helps the workforce with labor-intensive tasks, reducing human effort and speeding up production.
Blockchain
Automotive manufacturers, businesses, dealerships, and insurance companies handle millions of transactions daily. While transactions are mostly conducted online through banks, networks, or mobile devices, cybersecurity risks, lack of transparency, and excessive documentation hinder productivity.
Blockchain technology is a promising tool that enables seamless, hassle-free transactions. It prevents accidental data deletion or loss and integrates easily with existing technology frameworks. Blockchain is an excellent fraud prevention tool and can automate processes when necessary. Blockchain-based services can enhance current systems, making everything work more efficiently.
Industrial IoT (IIoT)
Industrial IoT is reshaping solutions for the new era of vehicles, bringing advanced connected car solutions and pushing innovation to unprecedented heights. Vehicle-to-vehicle (V2V) applications, Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS), vehicle-to-infrastructure (V2I) applications, in-car infotainment, predictive maintenance solutions, navigation and telematics, and vehicle-to-everything (V2X) communication—all highlight the immense potential IIoT has for designing and enhancing sophisticated automotive features.
Cloud Computing
Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs) in the automotive industry are leveraging cloud computing to improve production quality and efficiency. This technology introduces the concept of connected vehicles across all categories, from sales to after-sales services. Automotive suppliers use cloud computing to maximize uptime, improve first-time quality, and optimize productivity. Moreover, dealerships use cloud technology to reach and engage potential customers, monitor vehicle performance, and create customer service experiences. Thanks to cloud computing, today's consumers enjoy better shopping experiences, timely services, and greater variety.
IT-OT Convergence
IT/OT convergence is an integrated approach to controlling industrial operations, combining the overall technology framework with operational processes, integrating IT, hardware, and software.
Traditional siloed methods used by factory workers are now challenged, as Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs), Human-Machine Interfaces (HMIs), Industrial PCs, and automation controllers are installed at every touchpoint. Integrating modern functionalities into legacy systems has proven difficult, leading to inconsistent management. To avoid interoperability issues and inefficiencies, seamless integration between IT and OT frameworks is essential for producing flawless vehicles.
Smart Automation
Today's cars are essentially supercomputers on wheels. Modern vehicles are automated, equipped with numerous sensors and cameras, generating vast amounts of data. Smart automation collects, processes, analyzes, and disseminates this data and technology. Robotic process automation is essential on the automotive shop floor, handling everything from welding to assembly and painting. Even automotive financing and distribution are streamlined through automation.
From physical robots to digital robots, harnessing robotic process automation has become the current trend in the automotive industry. Robots are everywhere—from handling customer inquiries at contact centers, processing auto loans, arranging service appointments with dealers, sending alerts, running diagnostics, and even selling cars.
Let's go
The Impact of Industry 4.0 on Automotive Manufacturing
Final result
Flexibility
Digital transformation has led to a significant shift in consumer expectations—flexibility and agility are now the top priorities. In this fast-paced world, consumers seek flexible solutions over large-scale investments. The adoption of Industry 4.0 has made automotive industry processes and operations more flexible.
Efficiency
Automakers aim to enhance efficiency, and adopting Industry 4.0 practices seems to be the best choice. Augmented reality (AR) images of vehicle components or technical information optimize assembly processes, increase operational cost-effectiveness through prototyping, and reduce design costs. Additionally, AR-guided warehouse locators, automated processes for part storage, and product development increase productivity.
Agility
Higher production demands require the implementation of digital twins, automation, programmable robots, and predictive analytics. Industry 4.0 practices are agile and easily configurable with minimal human intervention.
Value chain outcome
Product Development Innovation
When visibility is critical, innovation thrives. OEMs and automakers can leverage Industry 4.0 to innovate designs, frameworks, processes, and practices, keeping them ahead of the competition.
Demand/Supply Planning
Predictive analytics for demand forecasting has been implemented across the industry and has proven beneficial. Automakers are now well-prepared to respond to sudden demand spikes or inventory backlogs.
Shop Floor Operations
With the growing adoption of AI, machine learning, IoT, and automation, even operations without Wi-Fi or proper infrastructure can stay connected. Track-and-trace capabilities can detect the movement of parts and equipment. Digital twins and blockchain technologies enable the exchange of vast amounts of information.
Supply Chain Optimization
Industry 4.0 has given rise to Supply Chain 4.0. As manufacturing becomes more localized, manufacturers are redesigning their supply chains, implementing best practices, and adopting emerging technologies.
After-Sales Services
Industry 4.0 features have significantly enhanced customer support and services, with field service operations helping manufacturers deliver a unified aftermarket experience. This, in turn, improves dealer responsiveness while reducing vehicle downtime.
Sales and Marketing
Handling customer inquiries, generating quality leads, automating contact centers, integrating AI and process automation into every aspect of marketing, and processing financial records—these ensure smoother operational flow.
Workplace Safety
As mentioned earlier, implementing robots, AI, and process automation fine-tunes various aspects of the work environment, ensuring safe and robust production.
Let's go
