China's Heavy Duty Truck (HDT) Market Faces Multiple Challenges.
After nearly a decade of rapid growth, the market saw a sharp downturn in 2022, with sales dropping 45% year-on-year. As the market stabilizes, several new trends are coming into play: the emergence and rise of new powertrains, partnerships exploring autonomous driving, an increase in exports, and customer pressure on pricing. What does this mean for China's HDT OEMs? This article explores these trends in the current market context and highlights opportunities for Chinese OEMs both domestically and internationally.
01
The Current Heavy Duty Truck Market in China
Several factors contribute to the current state of the Chinese HDT market.
Stable Market
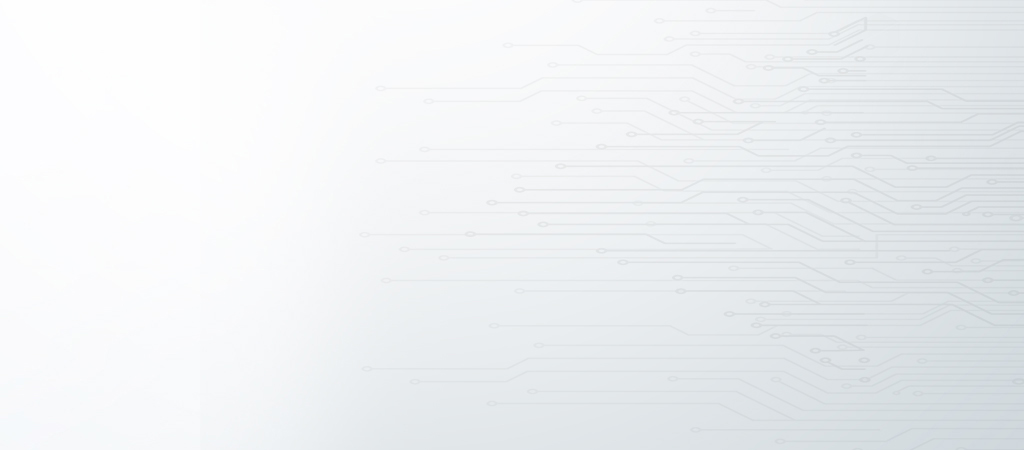
In 2023, driven by domestic market recovery and rising exports, sales in the Chinese HDT market slightly rebounded from the sharp decline of 2022, reaching about 900,000 trucks (including exports). Excluding exports, the domestic market saw sales of 616,000 trucks, benefiting from a rebound in key industries like logistics and China's economic recovery (Figure 1). In fact, China's GDP growth rate was 5% in 2023, compared to about 3% in 2022.
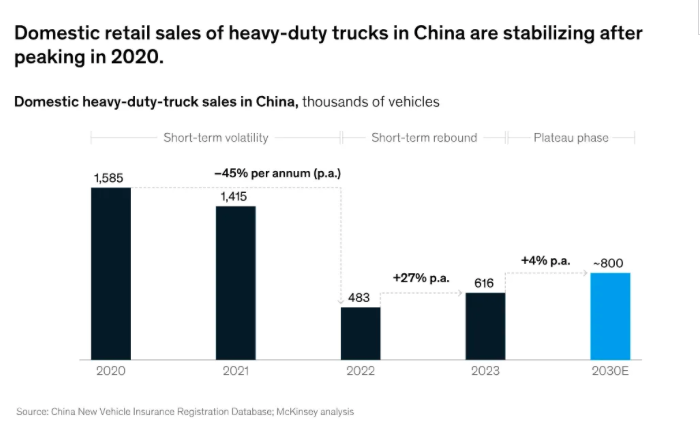
Image comes from internet
However, the market is not expected to fully return to the 2020 level of nearly 1.6 million trucks in the near future. Instead, based on various economic scenario analyses, truck growth is likely to stabilize at around 800,000 units, excluding exports. This is due to the slowdown in China's economy and downstream markets, a shift from road to rail transport to improve the overall efficiency of the logistics sector, and longer replacement cycles for HDTs as products mature.
Exports, however, are becoming an increasingly critical factor. By 2023, they contributed about 30% of the total market, amounting to 269,000 trucks, showing significant growth compared to previous years (Figure 2). Changes in both supply and demand have contributed to this. Chinese OEMs are shifting their strategic focus to global markets to cope with intensifying competition in the domestic market, where current demand and capacity are influencing competition.

Image comes from internet
The Emergence of New Powertrains
Tractors remain the most popular type of heavy-duty truck in China, accounting for about 43% of heavy truck sales in 2021, 48% in 2022, and 53% in 2023. Meanwhile, non-diesel powertrains are on the rise, making up about 30% of the market share by 2023 (Figure 3).
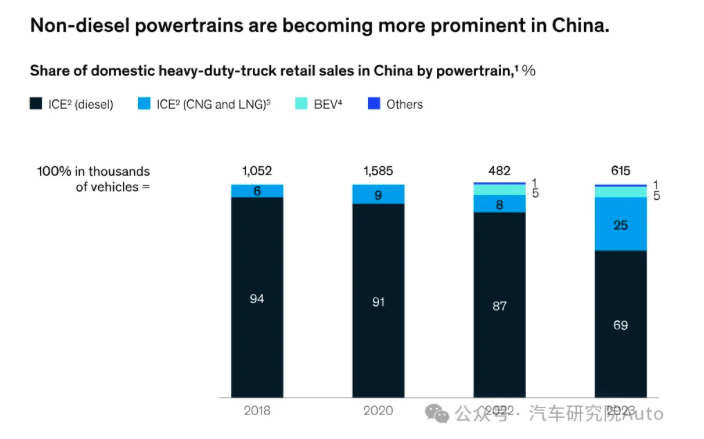
Image comes from internet
Thanks to low natural gas prices, compressed natural gas (CNG) and liquefied natural gas (LNG) took the largest share (25%). In 2023, the price ratio of diesel to natural gas rose from 1.4 times in 2022 to 1.9 times, improving the total cost of ownership (TCO) for drivers amid a relatively weak macroeconomic outlook. Major truck OEMs have also increased their focus on gasoline trucks, developing competitive new products.
Battery Electric Vehicles (BEVs) accounted for about 5% of domestic sales, with battery swapping accounting for around 48% of total sales. Battery swapping offers several advantages for market players:
-
For drivers and fleet owners, it provides a flexible purchase option, lowering the barrier to truck ownership. For example, drivers can purchase the chassis separately (excluding the battery) and obtain the battery through a leasing agreement. It also allows shorter charging times compared to charging HDTs, thus improving uptime. Currently, battery swapping for HDTs in China takes about 5 minutes, comparable to diesel trucks.
-
For battery owners, centralized battery management at swapping stations can extend battery life, enhancing profitability.
-
For OEMs, battery swapping HDTs are easier to promote than charging HDTs due to their cost competitiveness.
-
For infrastructure builders, fewer ultra-fast charging stations are needed, reducing grid challenges; ultra-fast charging stations for HDTs typically require charging capacities of over 1,000 kW.
By 2023, fuel cell electric vehicles (FCEVs) accounted for only about 0.6% of China's domestic HDT sales (or 3,612 trucks). The successful operation of battery swapping HDTs is likely to delay the widespread adoption of FCEV HDTs, given the cost and efficiency advantages of battery swapping.
Price Changes
From January 2018 to August 2023, the average transaction price of domestic heavy-duty trucks rose by about ¥42,000 (approximately $5,800). This was largely driven by the rising share of CNG/LNG trucks and BEVs, given that CNG/LNG trucks are about ¥80,000 more expensive than diesel trucks, while BEVs are priced on average ¥300,000 to ¥400,000 higher. McKinsey's analysis shows that the transaction price of diesel internal combustion engine (ICE) trucks has remained stable, despite cost increases associated with new emission and safety regulations and overall truck improvements (e.g., engine performance, cab setup, and display features).
Considering the producer price index (PPI), which grew by 6% in 2023 compared to 2018 as an estimate of inflation or producer prices, diesel ICE prices fell, likely due to intensified competition during periods of weak demand.
High Market Concentration
Market concentration remains high, with the top five OEMs accounting for about 88% of the market share. This trend is expected to continue over the next five years. The largest players are also expected to gain market share at the expense of smaller players, who have been losing market share in recent years. By 2023, international OEMs held about 1.0% of the domestic market, with localized products accounting for 0.4%.
Domestic market share growth has lagged behind expectations, as the pace of high-end development has been slower than anticipated, and business owners feel uncertain about the economy. However, more international OEMs are localizing their products, and these localized products are likely to become more cost-competitive over time, leading to an increase in market share for localized international products.
02
Trends That May Affect the Future of China’s HDT Market
Extended new powertrain
he new powertrains mentioned earlier are likely to quickly capture a significant share of the market. Due to the lower fuel costs of CNG and LNG compared to diesel, and their better emissions performance, these systems will continue to play an important role in the short term. BEV market share is expected to grow rapidly, reaching a penetration rate of 15% to 25% by 2030, supported by government initiatives and incentives. This growth will be driven by the introduction of advanced electric truck models from local OEMs, improved battery, electric powertrain, and autonomous driving (AD) technologies, better charging and battery-swapping infrastructure, and enhanced TCO competitiveness. Battery swapping is expected to become the dominant form of BEV in China, accounting for 60% to 70% of BEVs by 2030. While infrastructure has been a major challenge, ecosystem players are heavily investing in these developments.
Autonomous Driving
Chinese HDT OEMs are partnering with technology and logistics companies to pursue high-level autonomous driving (AD) applications, starting with specific use cases such as closed areas like ports and long-distance point-to-point highway transportation. For instance, one of China’s leading AD truck companies was authorized to conduct a pilot commercial deployment of AD HDTs on the inter-province logistics route between Beijing and Tianjin. This truck was co-developed through a strategic alliance between a Chinese logistics firm and a domestic truck OEM. Additionally, a Chinese truck OEM has been piloting commercial AD for HDTs in point-to-point scenarios at the Shanghai Port for about four years, a project co-developed with the OEM's AD technology subsidiary.
However, the road ahead poses significant challenges, particularly in achieving profitability, setting regulations (especially for long-distance AD applications), and overcoming technical obstacles that together may slow down the development of autonomous HDTs in China.
Increasing Exports
China’s leading HDT OEMs are actively seeking more growth opportunities and have announced ambitious export goals for 2024. Several factors are driving this shift. First, with the domestic market significantly smaller than in 2020, existing ICE truck production capacity in China is severely underutilized. OEMs may have opportunities to gain market share in price-sensitive markets. The shift to alternative power systems and new technologies like AD, coupled with different supply chain costs and incentives, creates opportunities for companies to become global leaders in new markets (e.g., by localizing electric truck production in some Southeast Asian countries). Finally, as seen in the passenger car sector, electrification opens additional export opportunities, as other market leaders may lose their value proposition (e.g., leading in fuel efficiency), creating room for new entrants.
Pricing Pressure
。Fleet owners are under
